Autonomous vehicles, often referred to as self-driving cars, are rapidly transforming the landscape of the automotive industry. As technology advances, these vehicles are becoming more prevalent on our roads, raising questions about their implications on various aspects of society. One significant area of concern and adaptation is the impact on auto insurance. In this article, we will explore the profound changes autonomous vehicles bring to the auto insurance industry, examining the challenges, opportunities, and potential shifts in the insurance landscape.
Contents:
- Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
- The Shift in Liability
- Impact on Premiums and Underwriting
- Evolving coverage models
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges
- Technological Innovation and Risk Mitigation
- The Future of Auto Insurance
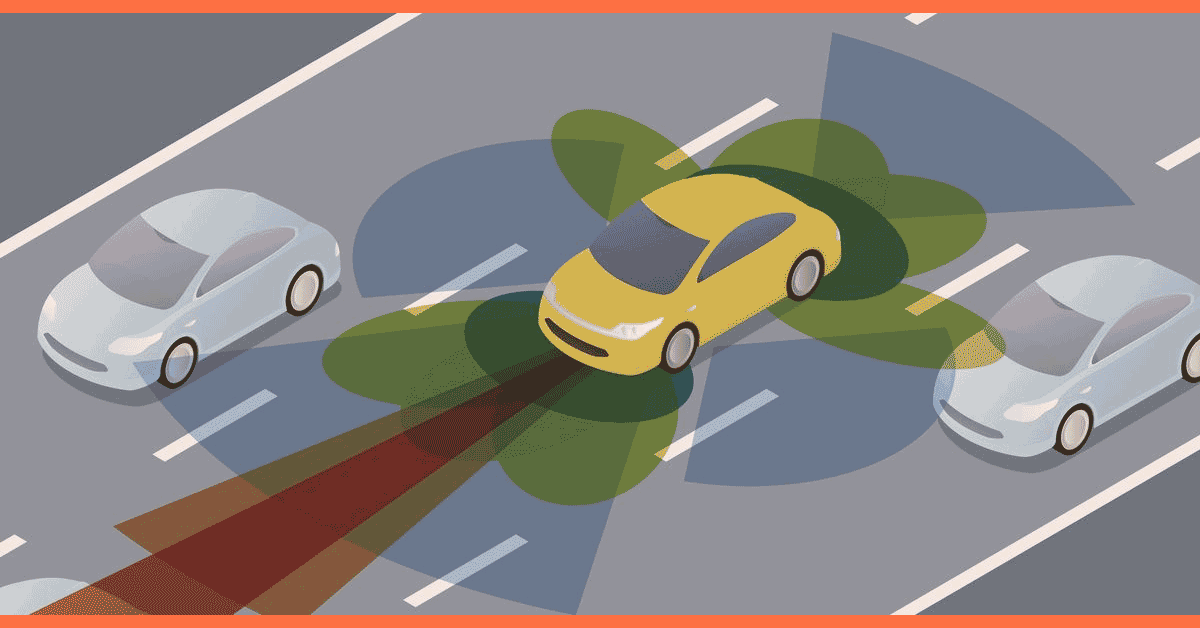
Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles utilize advanced technologies such as sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence to navigate the roads without human intervention. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined a taxonomy of autonomous driving levels, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). As vehicles progress through these levels, the role of the driver diminishes, and the vehicle assumes more responsibility for navigation.
The Shift in Liability
One of the fundamental changes brought about by autonomous vehicles is the shift in liability from human drivers to vehicle manufacturers and technology developers. In traditional auto insurance models, the driver’s behavior and history play a significant role in determining premiums and assessing liability. However, with autonomous vehicles, the responsibility for safe operation lies more with the technology and systems designed by manufacturers.
As a result, auto insurance may transition from individual policies covering drivers to policies that focus on the technology and software embedded in autonomous vehicles. Insurers will need to adapt their underwriting models to assess the risk associated with the technology, considering factors such as the vehicle’s software, sensors, and overall safety features.
Impact on Premiums and Underwriting
The introduction of autonomous vehicles is likely to influence insurance premiums and underwriting criteria. With the assumption that autonomous technologies reduce the risk of accidents caused by human error, premiums for traditional policies covering personal liability may decrease. However, premiums for policies covering the technology itself may increase as the value and complexity of the technology become critical factors.
Underwriters will need to develop new risk models that assess the reliability and safety of autonomous systems. Factors such as the vehicle’s software updates, cybersecurity measures, and adherence to industry standards will play a crucial role in determining insurance premiums. Additionally, underwriters may collaborate closely with manufacturers to gather real-time data on the performance and safety of autonomous vehicles.
Evolving Coverage Models
As autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, insurance coverage models will need to evolve to address emerging risks and liabilities. Coverage may shift from traditional policies covering accidents caused by human error to policies tailored for technology failures, cyber threats, and software malfunctions. Insurers may offer specialized coverage for incidents related to the autonomous driving system, including hardware failures, sensor malfunctions, or software glitches.
Moreover, the concept of “usage-based insurance” could gain prominence with autonomous vehicles. Insurers may analyze the data generated by these vehicles, such as driving patterns, traffic conditions, and the vehicle’s response to different scenarios, to personalize coverage and pricing. This shift towards more data-driven models could create a fairer and more accurate representation of risk.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The integration of autonomous vehicles into existing legal and regulatory frameworks poses substantial challenges. Determining liability in the event of an accident involving an autonomous vehicle may be complex, especially when multiple parties, including manufacturers, software developers, and human occupants, could be involved. Legal systems may need to adapt to account for the intricate nature of liability in autonomous driving scenarios.
Additionally, regulatory bodies will need to establish clear guidelines and standards for the testing, certification, and deployment of autonomous vehicles. These regulations should address issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and the ethical considerations of decision-making algorithms. Insurers will closely monitor and adapt to these regulatory developments to ensure compliance and provide comprehensive coverage.
Technological Innovation and Risk Mitigation
While autonomous vehicles introduce new risks, they also present opportunities for technological innovation that can enhance safety and risk mitigation. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and other safety features integrated into autonomous vehicles aim to reduce accidents and improve overall road safety. Insurers may incentivize the adoption of such technologies by offering discounts on premiums, creating a win-win situation for both policyholders and insurers.
Furthermore, the data collected by autonomous vehicles can be utilized to enhance risk modeling and predict potential issues before they escalate. Insurers may leverage telematics and artificial intelligence to gain insights into driver behavior, vehicle performance, and potential risks. This proactive approach can lead to more accurate underwriting and the prevention of potential accidents.
The Future of Auto Insurance
The impact of autonomous vehicles on auto insurance extends beyond individual policies and underwriting criteria. The very nature of auto insurance may undergo a transformation as vehicles become increasingly autonomous. Insurers may shift from a focus on individual drivers to collaborating with manufacturers and technology providers to ensure the safety and reliability of autonomous systems.
In the future, insurance products may encompass a broader ecosystem, covering not only individual vehicles but also the interconnected infrastructure that enables autonomous driving. Insurance models may evolve to provide comprehensive coverage for fleets of autonomous vehicles, mobility-as-a-service platforms, and shared autonomous transportation systems.
Conclusion
The advent of autonomous vehicles is ushering in a new era for the auto insurance industry. While the technology promises to enhance road safety and reduce accidents caused by human error, it also presents challenges in determining liability, adapting legal frameworks, and developing innovative insurance products. Insurers must stay agile and proactive in responding to these changes, collaborating with industry stakeholders to shape the future of auto insurance in the age of autonomy. As the technology continues to advance, the auto insurance landscape will evolve, offering opportunities for growth, innovation, and enhanced risk management.